ArrayList集合
2019/8/8约 1457 字大约 5 分钟
ArrayList源码示例
ArrayList集合
示例 1 : 使用数组的局限性
示例 2 : ArrayList存放对象
示例1:使用数组的局限性
如果要存放多个对象,可以使用数组,但是数组有局限性
比如 声明长度是10的数组
不用的数组就浪费了
超过10的个数,又放不下
//单纯的数组的增删改并不好操作,一旦操作起来,容器影响到其他元素的位置
//存10个英雄
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hero[] heros=new Hero[10];
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) {
heros[i]=new Hero("name:"+(i+1),100);
}
//打印
for(Hero hero:heros) {
System.out.println(hero);
}
//改血量,第八个名字改成name80,血量500
heros[7].setName("name80");
heros[7].setHp(500);
System.out.println(heros[7]);
//删除第八个
//..心态炸了,不写了
}
}
//定义好了一个英雄类
class Hero{
private String name;
private int hp;
public Hero(String name, int hp) {
this.name = name;
this.hp = hp;
}
public Hero() {
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getHp() {
return hp;
}
public void setHp(int hp) {
this.hp = hp;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Hero [name=" + name + ", hp=" + hp + "]";
}
}示例2: ArrayList存放对象
为了解决数组的局限性,引入容器类的概念。 最常见的容器类就是ArrayList
容器容量"capacity"会随着对象的增加,自动增长
只需要不断往容器里增加英雄即可,不用担心会出现数组的边界问题
arraylist的源码结构如下
package com.haoyu;
public class MyArrayList<E> {
private E[] data;
private int size;
// 构造函数,传入数组的容量capacity构造Array
public MyArrayList(int capacity) {
data = (E[]) new Object[capacity];
size = 0;
}
// 无参数的构造函数,默认数组的容量capacity=10
public MyArrayList() {
this(10);
}
// 获取数组的容量
public int getCapacity() {
return data.length;
}
// 获取数组中的元素个数
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
// 返回数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
// 在index索引的位置插入一个新元素e
public void add(int index, E e) {
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
if (size == data.length)
resize(2 * data.length);
for (int i = size - 1; i >= index; i--)
data[i + 1] = data[i];
data[index] = e;
size++;
}
// 向所有元素后添加一个新元素
public void addLast(E e) {
add(size, e);
}
// 在所有元素前添加一个新元素
public void addFirst(E e) {
add(0, e);
}
// 获取index索引位置的元素
public E get(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Index is illegal.");
return data[index];
}
// 修改index索引位置的元素为e
public void set(int index, E e) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Index is illegal.");
data[index] = e;
}
// 查找数组中是否有元素e
public boolean contains(E e) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (data[i].equals(e))
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 查找数组中元素e所在的索引,如果不存在元素e,则返回-1
public int find(E e) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (data[i].equals(e))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 从数组中删除index位置的元素, 返回删除的元素
public E remove(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
E ret = data[index];
for (int i = index + 1; i < size; i++)
data[i - 1] = data[i];
size--;
data[size] = null; // loitering objects != memory leak
if (size == data.length / 2)
resize(data.length / 2);
return ret;
}
// 从数组中删除第一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeFirst() {
return remove(0);
}
// 从数组中删除最后一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeLast() {
return remove(size - 1);
}
// 从数组中删除元素e
public void removeElement(E e) {
int index = find(e);
if (index != -1)
remove(index);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Array: size = %d , capacity = %d\n", size, data.length));
res.append('[');
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
res.append(data[i]);
if (i != size - 1)
res.append(", ");
}
res.append(']');
return res.toString();
}
// 将数组空间的容量变成newCapacity大小
private void resize(int newCapacity) {
E[] newData = (E[]) new Object[newCapacity];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
newData[i] = data[i];
data = newData;
}
}引入arraylist的泛型使用方式,解决代码不好看问题
//import java.util.ArrayList;
//Hero[] heros=new Hero[10];----不用去定义初始长度,arraylist自动增加长度capacity
//泛型的第一次接触 <> 泛型符号
ArrayList<Hero> heros2=new ArrayList<Hero>();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) {
heros2.add(new Hero("name:"+(i+1),100));
// heros2.add(1);
}
// for(int i=0;i<heros2.size();i++) {
// System.out.println(heros2.get(i));//i--0开始 i<size
// }
for(Hero hero:heros2) {
System.out.println(hero);
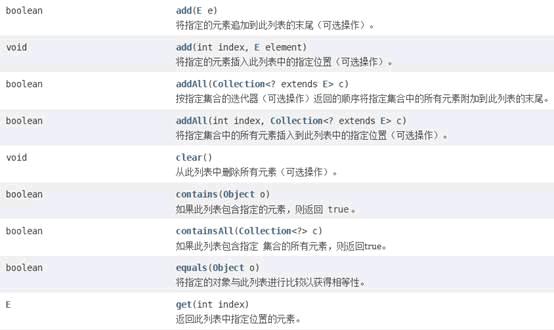
}示例3:arraylist常用方法
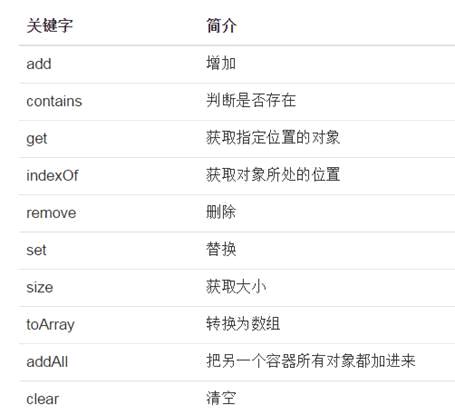
类似操作自行实现
// ArrayList-使用泛型操作
ArrayList<Hero> hero = new ArrayList<Hero>();
ArrayList<Hero> heroTo = new ArrayList<Hero>();
Hero hero1 = new Hero("hero1", 111);
Hero hero2 = new Hero("hero2", 222);
Hero hero3 = new Hero("hero3", 333);
Hero hero0 = new Hero("heroTo", 0);
Hero herot = new Hero("heroT2", 2);
// 在,末尾添加元素
heroTo.add(hero0);
heroTo.add(herot);
hero.add(hero1);
hero.add(hero2);
hero.add(hero3);
hero.add(new Hero("hero4", 444));
// 指定下标添加元素
hero.add(4, new Hero("indexhero1", 555));
for (Hero h : hero) {
System.out.println(h);// h.getHp();h.getName();
}
// 添加到另外一个集合中addAll(Object);addAll(index,Object);
heroTo.addAll(1, hero);
for (Hero h : heroTo) {
System.out.println(h);// h.getHp();h.getName();
}
// 清空列表所有元素
// hero.clear();
// 查看数组元素个数
System.out.println("size-->" + hero.size());
// 判断是否存在元素contains
System.out.println("contains-->" + hero.contains(hero.get(2)));//
boolean filg = hero.contains(hero2);
System.out.println("contains-->" + filg);
// containsAll() 如果此列表包含指定集合的所有元素,则返回true。
boolean filg2 = heroTo.containsAll(hero);// true
System.out.println("containsAll-->" + filg2);
// equals() 指定的对象与此列表进行相等性比较。
boolean filg3 = hero3.equals(hero3);
System.out.println("equals-->" + filg3);
// 获取指定位置的元素 数组.get()
System.out.println("get-->" + hero.get(1));
// 根据对象获取元素下标 数组.indexOf()
int index = hero.indexOf(hero3);
System.out.println("getindexOf-->" + index);
// 设置元素set
hero.set(1, new Hero("setname", 999));
// 删除元素remove(int index);remove(Object o)
hero.remove(2);// 通过索引
hero.remove(hero1);// 通过元素
// removeAll() 从该列表中删除指定集合中包含的所有元素(可选操作)。
// hero.removeAll(hero);
for (Hero h : hero) {
System.out.println(h);// h.getHp();h.getName();
}
System.out.println("size-->" + hero.size());
heroTo.toArray();
for (Hero h : heroTo) {
System.out.println(h);// h.getHp();h.getName();}示例4:list接口
List<Hero> heros3=new ArrayList<Hero>();
更新日志
2026/1/9 00:55
查看所有更新日志
59d7d-于e2e3a-于