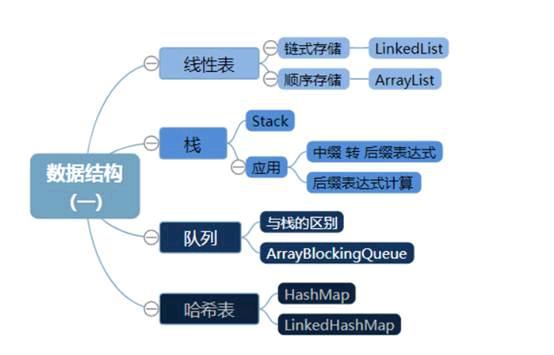
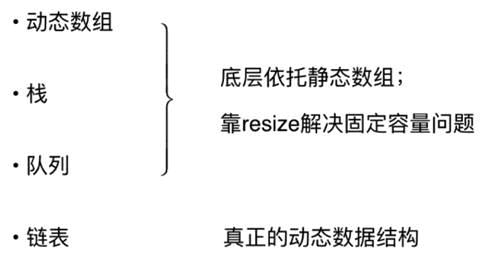
数据结构
数组基础、栈、队列、链表
数组基础
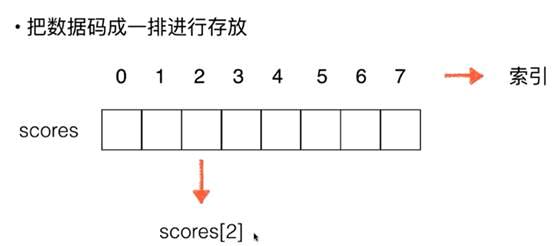
给数组取一个名字Array ——arr
真实环境中更需要给数组取一个有实际意义的名字
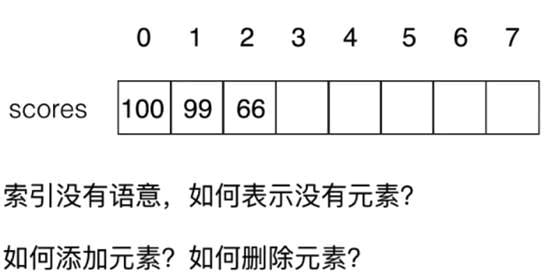
数据的索引
索引概念很重要,可以有语义也可以没有语义
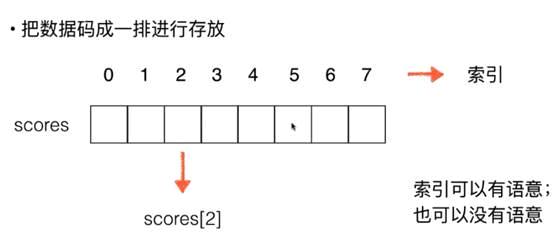
对于索引的理解
1, 数组的最大优点:快速查询——scores【2】
2, 数组最好应用于“索引有语意”的情况
3, 但并非所有有语意的索引都适用于数组
身份证号:50010520189898
4, 数组也可以处理索引没有语意的情况
5, 本章处理主要就是处理“索引没有语意”的情况数组的使用
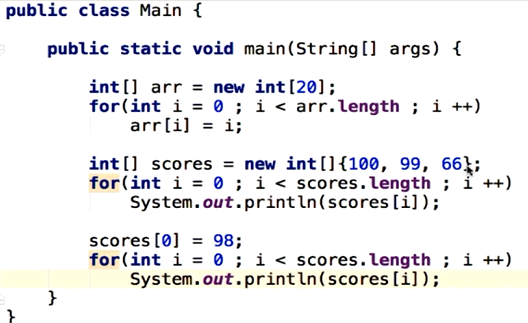
需求:遍历数组,打印一个班的成绩
封装数组
提出需求:需要基于java数组,二次封装属于我们自己的数组类,区别于java本身的静态数组,性能媲美静态数组
动态数组设计过程

Capacity:容量
V1.0版本:基础数组结构
class MyArray{
//私有化数据
private int[] data;
//定义长度
private int size;
//构造函数,传入数组的容量capacity构造array
public MyArray(int capacity){
data=new int[capacity];
size=0;
}
//无参构造函数,默认数组的容量capacity=10
public MyArray(){
this(10);
}
//获取数组中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
//获取数组容量
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length;
}
//返回数组是为空 不是 为空 非空 为空 true
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size==0;
}
}
V1.1版本:向数组中添加元素
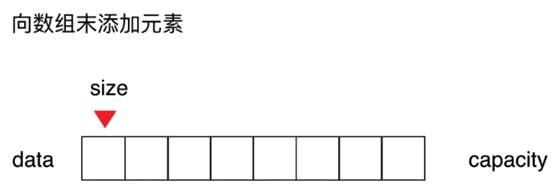
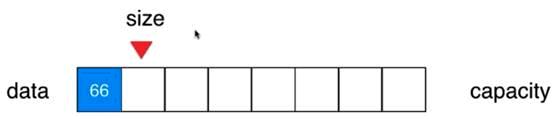
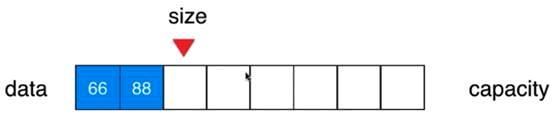
//向所有元素后添加一个新元素
public void addLast(int e){
if(size==data.length)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("addlast faild,array is full");
// data[size++]=e;不便于阅读
data[size]=e;
size++;
}
V1.2版本:向指定的位置插入指定的元素,提供一个addFirst
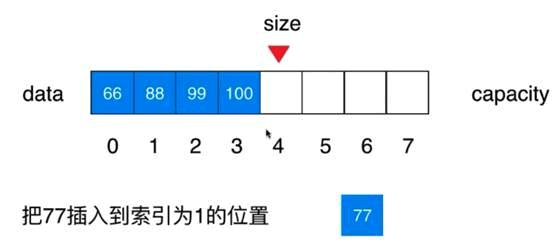
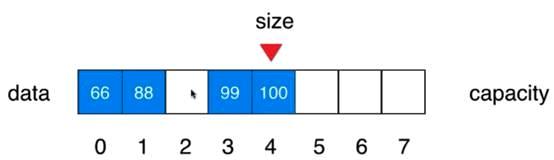
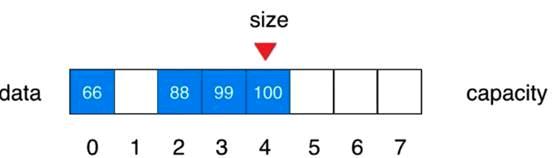
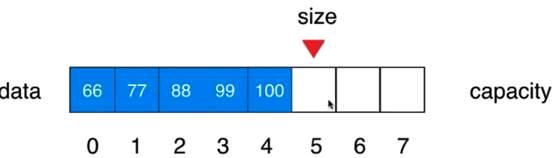
代码写完后需要修改刚才的增加函数
//向所有元素后添加一个新元素
public void addLast(int e){
// if(size==data.length)
// throw new IllegalArgumentException("addlast faild,array is full");
//// data[size++]=e;不便于阅读
// data[size]=e;
// size++;
add(size, e);
}
// 在所有元素前添加一个新元素
public void addFirst(int e){
add(0, e);
}
// 在index索引的位置插入一个新元素e
public void add(int index, int e){
if(size == data.length)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Array is full.");
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
for(int i = size - 1; i >= index ; i --)
data[i + 1] = data[i];
data[index] = e;
size ++;
}
V1.3版本:在数组中查询元素和修改元素
// 获取index索引位置的元素
public int get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Index is illegal.");
return data[index];
}
// 修改index索引位置的元素为e
public void set(int index, int e){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Index is illegal.");
data[index] = e;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Array: size = %d , capacity = %d\n", size, data.length));
res.append('[');
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
res.append(data[i]);
if(i != size - 1)
res.append(", ");
}
res.append(']');
return res.toString();
}
V1.4版本:包含搜索和删除
// 查找数组中是否有元素e
public boolean contains(int e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i] == e)
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 查找数组中元素e所在的索引,如果不存在元素e,则返回-1
public int find(int e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i] == e)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 从数组中删除index位置的元素, 返回删除的元素
public int remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
int ret = data[index];
for(int i = index + 1 ; i <= size ; i ++)
data[i - 1] = data[i];
size --;
return ret;
}
// 从数组中删除第一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public int removeFirst(){
return remove(0);
}
// 从数组中删除最后一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public int removeLast(){
return remove(size - 1);
}
// 从数组中删除元素e
public void removeElement(int e){
int index = find(e);
if(index != -1)
remove(index);
}
V1.5版本:使用泛型
理由:

代码改造:Array
package com.haoyu;
public class Array<E> {
private E[] data;
private int size;
// 构造函数,传入数组的容量capacity构造Array
public Array(int capacity){
data = (E[])new Object[capacity];
size = 0;
}
// 无参数的构造函数,默认数组的容量capacity=10
public Array(){
this(10);
}
// 获取数组的容量
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length;
}
// 获取数组中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 在index索引的位置插入一个新元素e
public void add(int index, E e){
if(size == data.length)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Array is full.");
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
for(int i = size - 1; i >= index ; i --)
data[i + 1] = data[i];
data[index] = e;
size ++;
}
// 向所有元素后添加一个新元素
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
// 在所有元素前添加一个新元素
public void addFirst(E e){
add(0, e);
}
// 获取index索引位置的元素
public E get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Index is illegal.");
return data[index];
}
// 修改index索引位置的元素为e
public void set(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Index is illegal.");
data[index] = e;
}
// 查找数组中是否有元素e
public boolean contains(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 查找数组中元素e所在的索引,如果不存在元素e,则返回-1
public int find(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 从数组中删除index位置的元素, 返回删除的元素
public E remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
E ret = data[index];
for(int i = index + 1 ; i < size ; i ++)
data[i - 1] = data[i];
size --;
data[size] = null; // loitering objects != memory leak
return ret;
}
// 从数组中删除第一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeFirst(){
return remove(0);
}
// 从数组中删除最后一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeLast(){
return remove(size - 1);
}
// 从数组中删除元素e
public void removeElement(E e){
int index = find(e);
if(index != -1)
remove(index);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Array: size = %d , capacity = %d\n", size, data.length));
res.append('[');
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
res.append(data[i]);
if(i != size - 1)
res.append(", ");
}
res.append(']');
return res.toString();
}
}
测试类:student
package com.haoyu;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int score;
public Student(String studentName, int studentScore){
name = studentName;
score = studentScore;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return String.format("Student(name: %s, score: %d)", name, score);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Array<Student> arr = new Array<Student>();
arr.addLast(new Student("Alice", 100));
arr.addLast(new Student("Bob", 66));
arr.addLast(new Student("Charlie", 88));
System.out.println(arr);
}
}
打印类:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Array<Integer> arr = new Array<Integer>(20);
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++)
arr.addLast(i);
System.out.println(arr);
arr.add(1, 100);
System.out.println(arr);
arr.addFirst(-1);
System.out.println(arr);
// [-1, 0, 100, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
arr.remove(2);
System.out.println(arr);
arr.removeElement(4);
System.out.println(arr);
arr.removeFirst();
System.out.println(arr);
}
}
V1.5版本:动态数组
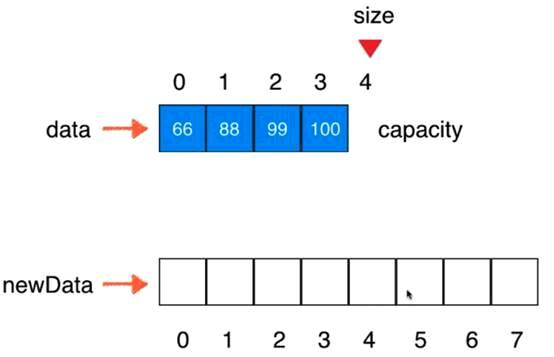
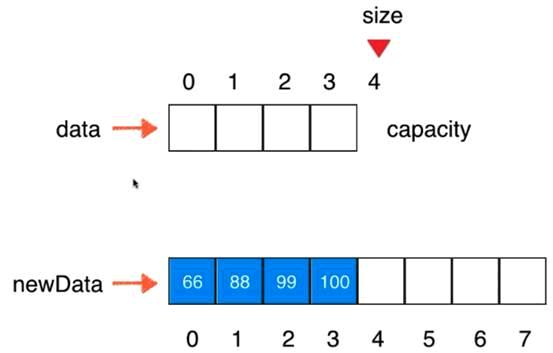
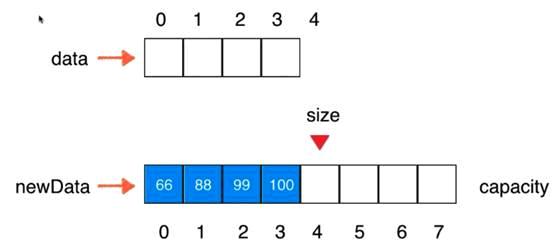
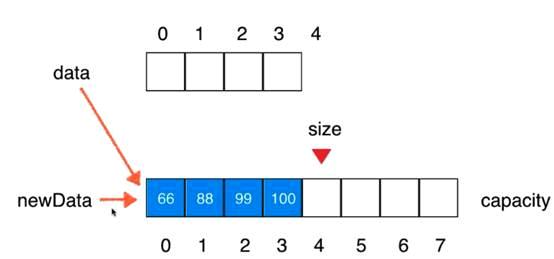
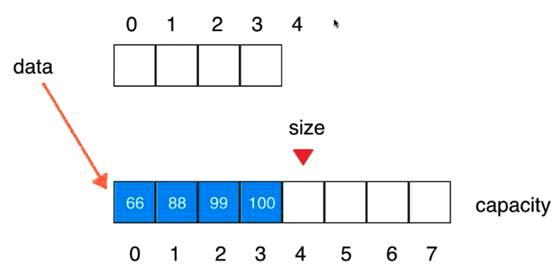
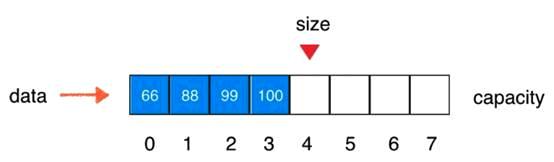
// 在index索引的位置插入一个新元素e
public void add(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
if(size == data.length)
resize(2 * data.length);
for(int i = size - 1; i >= index ; i --)
data[i + 1] = data[i];
data[index] = e;
size ++;
}
// 将数组空间的容量变成newCapacity大小
private void resize(int newCapacity){
E[] newData = (E[])new Object[newCapacity];
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++)
newData[i] = data[i];
data = newData;
}
测试:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Array<Integer> arr = new Array<Integer>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++)
arr.addLast(i);
System.out.println(arr);
arr.add(1, 100);
System.out.println(arr);
arr.addFirst(-1);
System.out.println(arr);
arr.remove(2);
System.out.println(arr);
arr.removeElement(4);
System.out.println(arr);
arr.removeFirst();
System.out.println(arr);
}
}
V1.51经典版程序
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* <p>Title: Demo19.java</p>
* <p>Description:
* 125经典版 </p>
* <p>Copyright: Copyright (c) 2017</p>
* <p>Company: com.haoyu</p>
* @author 大师
* @date 2019年8月14日
* @version 1.0
*/
//定义集合--多功能的简便操作的数组
//my 我的 array 数组 list 列表
//我的数组增强功能后的列表类--线性数组集合类
class MyArrayList{
//声明要准备好空间,等待后面存入元素
private int[] data;
//定义元素个数
private int size;
//定义一个初始化数组容量大小
private int capacity=16;
//new的时候保证初始化空间与个数
public MyArrayList(int capacity) {
//更改初始化的长度
//健壮性判断
if(capacity<=0) {
data=new int[this.capacity];
}else {
data=new int[capacity];
}
//由于现在没有存储元素,因此元素个数=0
this.size=0;
}
//无参构造函数,默认数组的容量capacity=10
public MyArrayList(){
//调用其他的带参数的对应构造函数
this(10);
}
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
//获取数组容量--数组定义后开辟的空间个数
public int getCapacity(){
//数组在初始化后就开辟的空间个数,只不过里面目前有没有元素。不清楚
return data.length;
}
//返回数组"是为空" false isEmpty-不为空 true isEmpty-为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size==0;
}
//在数组末尾增加元素
//last 最后 e-element:元素
//MyArrayList [data=[1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]
// public void addLast(int e) {
// //判断一下当前的空间是否已经容量满员。如果已经满员了,就不应该执行增加操作了
// if(size==data.length) {
// //一旦出现问题,throw 抛出去一个问题 xxxException exception:异常,问题
// //后面的java代码不会再继续执行
// throw new RuntimeException("容量已满");
// }
// //size当前位置增加一个元素(赋值一个元素)
// data[size]=e;
// //size往后走一位
// size++;
// }
public void addLast(int e) {
insert(size,e);
}
public void addFirst(int e) {
insert(0,e);
}
//插入元素 index=插入的位置--数组元素角标
//index-0 +++ e-element:元素
public void insert(int index,int e) {
//判断一下当前的空间是否已经容量满员。如果已经满员了,就不应该执行增加操作了
if(size==data.length) {
//一旦出现问题,throw 抛出去一个问题 xxxException exception:异常,问题
//后面的java代码不会再继续执行
// throw new RuntimeException("容量已满");
resize(2*data.length);
}
//插歪了,让代码停止执行
if(index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
}
//MyArrayList [data=[1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]
//size=3
//i=size-1=2 data[2]=3
//i-- i>=index index=0
//2 1 0:存在元素要依次往后走一位 e=data[index=0]
for(int i=size-1;i>=index;i--) {
data[i+1]=data[i];
}
//剩下的[index]=e
data[index]=e;
//由于是增加了一个元素
size++;
if(size==data.length) {
resize(2*data.length);
}
}
//获取元素 index-0~size-1
public int get(int index) {
//查歪了
if(index < 0 || index > size-1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
}
return data[index];
}
//修改制定位置的元素
public void set(int index,int e) {
//查歪了
if(index < 0 || index > size-1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
}
data[index]=e;
}
//查看数组是否包含元素
public boolean contains(int e) {
//从0角标开始往后遍历,直到size-1结束
for(int i=0;i<size;i++) {
if(data[i]==e) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//获取索引角标
//如果不在范围内,返回-1
public int getIndex(int e) {
for(int i=0;i<size;i++) {
if(data[i]==e) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 从数组中删除index位置的元素, 返回删除的元素
public int remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
int ret = data[index];
for(int i = index + 1 ; i <= size ; i ++)
data[i - 1] = data[i];
size --;
// 1 2 3 4 5 0 0 0 size:5 length:8
// 1 2 3 4 0 0 0 0 size:4 length:8
// 1 2 3 0 size:3 length:4
if(size==data.length/2-1) {
delResize();
}
return ret;
}
//扩容操作 re再一次 size大小 resize再一次确定大小
//2*data.length
public void resize(int newCapacity) {
int[] newData=new int[newCapacity];
//把原来少元素的数组赋值给长的数组
for(int i=0;i<data.length;i++) {
newData[i]=data[i];
}
data=newData;//数组名字指向的是整个数组的内存起始地址
}
//缩容操作
public void delResize() {
int[] newData=new int[data.length/2];
for(int i=0;i<newData.length;i++) {
newData[i]=data[i];
}
data=newData;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyArrayList [data=" + Arrays.toString(data) + "]";
}
}
V1.6版本:使用泛型
public class Array<E> {
private E[] data;
private int size;
// 构造函数,传入数组的容量capacity构造Array
public Array(int capacity){
data = (E[])new Object[capacity];
size = 0;
}
// 无参数的构造函数,默认数组的容量capacity=10
public Array(){
this(10);
}
// 获取数组的容量
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length;
}
// 获取数组中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 在index索引的位置插入一个新元素e
public void add(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
if(size == data.length)
resize(2 * data.length);
for(int i = size - 1; i >= index ; i --)
data[i + 1] = data[i];
data[index] = e;
size ++;
}
// 向所有元素后添加一个新元素
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
// 在所有元素前添加一个新元素
public void addFirst(E e){
add(0, e);
}
// 获取index索引位置的元素
public E get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Index is illegal.");
return data[index];
}
// 修改index索引位置的元素为e
public void set(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Index is illegal.");
data[index] = e;
}
// 查找数组中是否有元素e
public boolean contains(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 查找数组中元素e所在的索引,如果不存在元素e,则返回-1
public int find(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 从数组中删除index位置的元素, 返回删除的元素
public E remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
E ret = data[index];
for(int i = index + 1 ; i < size ; i ++)
data[i - 1] = data[i];
size --;
data[size] = null; // loitering objects != memory leak
if(size == data.length / 2)
resize(data.length / 2);
return ret;
}
// 从数组中删除第一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeFirst(){
return remove(0);
}
// 从数组中删除最后一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeLast(){
return remove(size - 1);
}
// 从数组中删除元素e
public void removeElement(E e){
int index = find(e);
if(index != -1)
remove(index);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Array: size = %d , capacity = %d\n", size, data.length));
res.append('[');
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
res.append(data[i]);
if(i != size - 1)
res.append(", ");
}
res.append(']');
return res.toString();
}
// 将数组空间的容量变成newCapacity大小
private void resize(int newCapacity){
E[] newData = (E[])new Object[newCapacity];
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++)
newData[i] = data[i];
data = newData;
}
}
数组时间复杂度算法简单分析
1, 简单复杂度分析
通过时间复杂度分析出算法的性能如何
时间复杂度通常是如下表示的
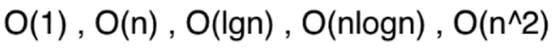
读作大O1 大On大O nlogn 大On平方
这里的这个大O就是描述的算法的运行时间和输入数据之间的关系
什么是运行时间和输入数据之间的关系呢?通过下面例子来演示

也就是说这里产生了n个数,那么n的数量是多少,对应的时间也就线性增加,但其实,每个n并非是时间系数为1的.
比如:操作每一个数(temp),需要从这个这个数组中通过for循环取出来,然后需要取出sum并与temp加在一起重新再赋值给sum,对于每个数其实都是需需要这么多操作的,那么这样的操作所花费的时间系数,我们称之为C1,那么在开始计算之前可能还需要赋值sum=0,完成计算后还要返回这个sum,这些每次都有的操作所花费的等同的时间叫做c2
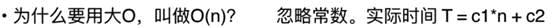
为什么要忽略这个c1,c2呢,因为拿这里的c1来说,就算是直接使用,基于不同的语言,执行时间段也是不同的,就算是执行时间相同,底层的操作系统的汇编层面或者机器语言所花费的解析时间也不同,而且不同的cpu也是不同的,因此c2也是同理。接下来看一组结论和案例对比:
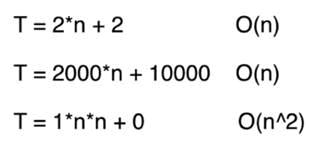

这里的时间复杂度描述的不是临界值,而是n趋近于无穷时候,这个算法谁块谁慢,同理,在这种情况下,低阶项实际上也很小,可以看做也是一个常数,忽略不计
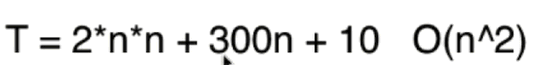
分析自定义数组的各项操作

针对删除操作,删除1个跟删除n个平均来看,就是n/2,1/2也是一个常数系数,舍去系数O(n)
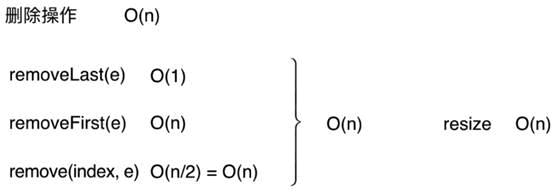

结论:
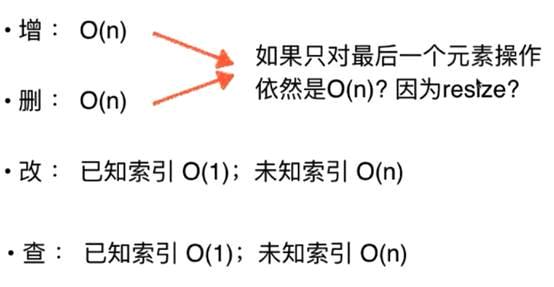
问题:删除和增加的分析完全使用最坏时间复杂度来分析是不合理的,因为并不是所有的操作都会触发这个容积的扩容
2, 均摊复杂度和防止复杂度的震荡
分析增加操作中触发resize操作的条件
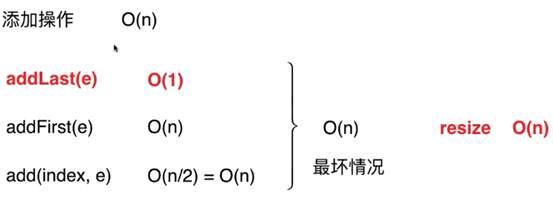
分析:假如一个数组的capacity是10个元素,那么添加10个元素才可能会触发一次resize,此时触发resize之后数组的容量就会变成20,此时再添加10个才会再次触发这个resize,这个时候会变成capacity为40,也就是再添加20个数,才会触发resize,也就是说不会是每次添加一个元素都会触发resize,而我们却一直用最坏时间复杂度分析,这样是不合理的
再次深入分析,案例如下:
在resize之前,所有的操作都是O(1)级别,而在addlast为第9个时候需要扩容,那么第九次等于for循环所有数组里的值进入新数组的时间和,再加1次add操作
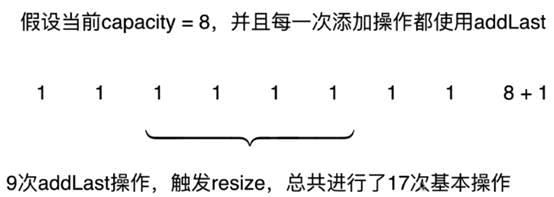
所以,对于addLast来说,9次操作,平均来讲,每次的操作接近2次基本操作
结论

这样均摊计算,时间复杂度是O(1)级别,在这样的例子里,这样均摊计算比计算最坏情况有意义

按照这样理解removeLast的均摊时间复杂度也是O(1)级别
但是这样会引发下一个问题
3,复杂度震荡
初始条件
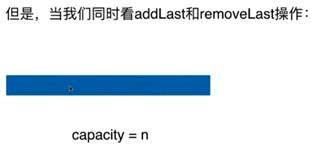
这个时候增加一个元素,触发的是扩容操作,加一个元素
马上又进行removeLast的操作,此时又会触发缩容的操作,再次调用resize,时间复杂度依然是O(n)

一直这样循环呢?

解决办法
扩容没有办法减少时间复杂度的增加,但是缩小的时候,并不着急把扩到二倍的数组容量减少为原来的1倍,同理这个时候要扩容也不用再次O(n)的addLast操作而是O(1)
当全部元素只剩下原来的4分1,也就是说

public class Array<E> {
private E[] data;
private int size;
// 构造函数,传入数组的容量capacity构造Array
public Array(int capacity){
data = (E[])new Object[capacity];
size = 0;
}
// 无参数的构造函数,默认数组的容量capacity=10
public Array(){
this(10);
}
// 获取数组的容量
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length;
}
// 获取数组中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 在index索引的位置插入一个新元素e
public void add(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
if(size == data.length)
resize(2 * data.length);
for(int i = size - 1; i >= index ; i --)
data[i + 1] = data[i];
data[index] = e;
size ++;
}
// 向所有元素后添加一个新元素
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
// 在所有元素前添加一个新元素
public void addFirst(E e){
add(0, e);
}
// 获取index索引位置的元素
public E get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Index is illegal.");
return data[index];
}
// 修改index索引位置的元素为e
public void set(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Index is illegal.");
data[index] = e;
}
// 查找数组中是否有元素e
public boolean contains(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 查找数组中元素e所在的索引,如果不存在元素e,则返回-1
public int find(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 从数组中删除index位置的元素, 返回删除的元素
public E remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
E ret = data[index];
for(int i = index + 1 ; i < size ; i ++)
data[i - 1] = data[i];
size --;
data[size] = null; // loitering objects != memory leak
//对于动态数组来说,不能够在缩容的时候让他的值等于0
if(size == data.length / 4 && data.length / 2 != 0)
resize(data.length / 2);
return ret;
}
// 从数组中删除第一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeFirst(){
return remove(0);
}
// 从数组中删除最后一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeLast(){
return remove(size - 1);
}
// 从数组中删除元素e
public void removeElement(E e){
int index = find(e);
if(index != -1)
remove(index);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Array: size = %d , capacity = %d\n", size, data.length));
res.append('[');
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
res.append(data[i]);
if(i != size - 1)
res.append(", ");
}
res.append(']');
return res.toString();
}
// 将数组空间的容量变成newCapacity大小
private void resize(int newCapacity){
E[] newData = (E[])new Object[newCapacity];
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++)
newData[i] = data[i];
data = newData;
}
}
栈(stack)
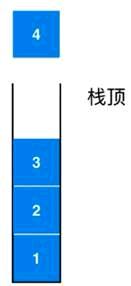
Stack是一种线性结构
相比数组,栈对应的操作是数组的子集,而且他的操作更少
只能从唯一的一端添加元素,也只能从这个唯一的一端取出元素
这个唯一的一端称为栈顶
展示元素入栈的过程
3这个元素只能在这个位置,不可以插入2和1元素之间
展示元素出栈的过程
小结
1, 栈是一种后进先出的数据结构
2, Last In First Out(LIFO)
3, Stack在计算机的运用里拥有不可思议的作用
案例1
沉迷学习无法自拔

最直接的一个案例,比如word中的文字撤销操作,比如以下的撤销不法,当这个不法两个字被撤销后,不需要再保留他们,直接出栈

输入正确的内容和顺序

案例2
程序调用的系统栈
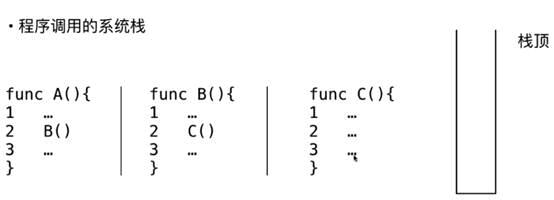
首先执行A这个函数
顺序执行1,2,3,行,当在执行到第二行的时候
会跳去执行B这个函数,a函数会暂时中断
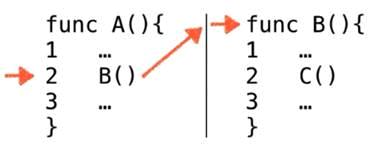
此时可以在系统栈中认为,A函数执行到了第二行,记为A2
然后继续执行
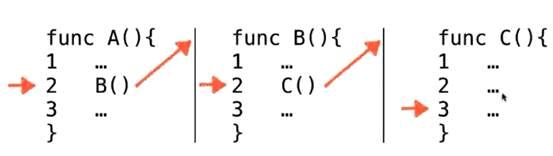
同理
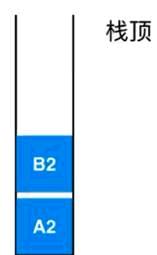
最后C函数在执行完成之后,就会回到B2继续执行,然后执行完成,B2出栈,剩下一个A2,继续执行A函数的内容最后A2出栈函数全部执行完毕
栈的基本实现

栈的实现有很多种数据结构的方式,数组实现只是其中一种

栈的实现结构

对应的array的数组,增加部分加粗标红
Array
public class Array<E> {
private E[] data;
private int size;
// 构造函数,传入数组的容量capacity构造Array
public Array(int capacity){
data = (E[])new Object[capacity];
size = 0;
}
// 无参数的构造函数,默认数组的容量capacity=10
public Array(){
this(10);
}
// 获取数组的容量
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length;
}
// 获取数组中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 在index索引的位置插入一个新元素e
public void add(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
if(size == data.length)
resize(2 * data.length);
for(int i = size - 1; i >= index ; i --)
data[i + 1] = data[i];
data[index] = e;
size ++;
}
// 向所有元素后添加一个新元素
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
// 在所有元素前添加一个新元素
public void addFirst(E e){
add(0, e);
}
// 获取index索引位置的元素
public E get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Index is illegal.");
return data[index];
}
public E getLast(){
return get(size - 1);
}
public E getFirst(){
return get(0);
}
// 修改index索引位置的元素为e
public void set(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Index is illegal.");
data[index] = e;
}
// 查找数组中是否有元素e
public boolean contains(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 查找数组中元素e所在的索引,如果不存在元素e,则返回-1
public int find(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 从数组中删除index位置的元素, 返回删除的元素
public E remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
E ret = data[index];
for(int i = index + 1 ; i < size ; i ++)
data[i - 1] = data[i];
size --;
data[size] = null; // loitering objects != memory leak
if(size == data.length / 4 && data.length / 2 != 0)
resize(data.length / 2);
return ret;
}
// 从数组中删除第一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeFirst(){
return remove(0);
}
// 从数组中删除最后一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeLast(){
return remove(size - 1);
}
// 从数组中删除元素e
public void removeElement(E e){
int index = find(e);
if(index != -1)
remove(index);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Array: size = %d , capacity = %d\n", size, data.length));
res.append('[');
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
res.append(data[i]);
if(i != size - 1)
res.append(", ");
}
res.append(']');
return res.toString();
}
// 将数组空间的容量变成newCapacity大小
private void resize(int newCapacity){
E[] newData = (E[])new Object[newCapacity];
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++)
newData[i] = data[i];
data = newData;
}
}
Stack
public interface Stack<E> {
int getSize();
boolean isEmpty();
void push(E e);
E pop();
E peek();
}
ArrayStack
public class ArrayStack<E> implements Stack<E> {
private Array<E> array;
public ArrayStack(int capacity){
array = new Array<>(capacity);
}
public ArrayStack(){
array = new Array<>();
}
@Override
public int getSize(){
return array.getSize();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty(){
return array.isEmpty();
}
public int getCapacity(){
return array.getCapacity();
}
@Override
public void push(E e){
array.addLast(e);
}
@Override
public E pop(){
return array.removeLast();
}
@Override
public E peek(){
return array.getLast();
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append("Stack: ");
res.append('[');
for(int i = 0 ; i < array.getSize() ; i ++){
res.append(array.get(i));
if(i != array.getSize() - 1)
res.append(", ");
}
res.append("] top");
return res.toString();
}
}
Main
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayStack<Integer> stack = new ArrayStack<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i ++){
stack.push(i);
System.out.println(stack);
}
stack.pop();
System.out.println(stack);
}
}
栈的时间复杂度分析
Stack案例实操(编译器对括号的匹配报错机制)
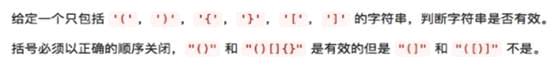
分析思路
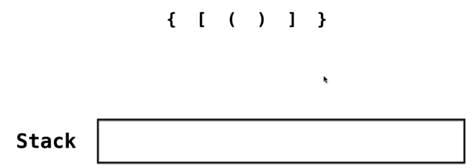
逐一加入栈结构
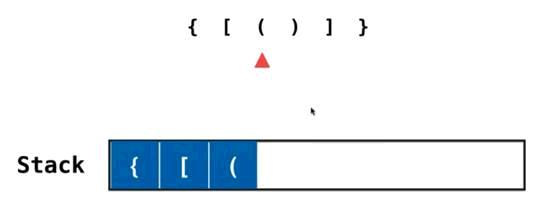
当开始匹配右括号的时候,需要看当前栈顶是否是和他匹配的,如果匹配那么当前栈顶的括号就可以出栈了
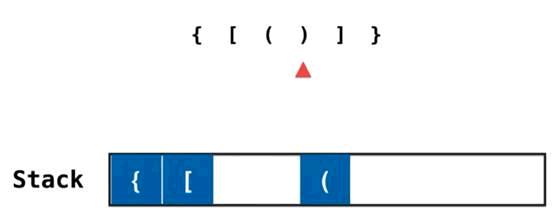
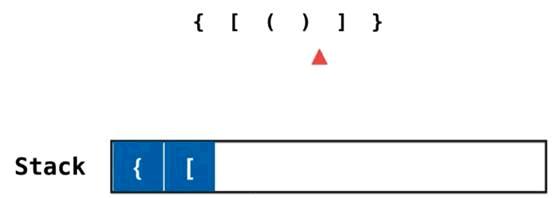
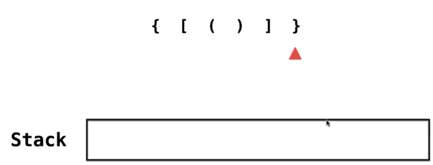
当全部出栈,那么当前的匹配就是一个合法的字符串
代码实现
import java.util.Stack;
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < s.length() ; i ++){
char c = s.charAt(i);
if(c == '(' || c == '[' || c == '{')
stack.push(c);
else{
if(stack.isEmpty())
return false;
char topChar = stack.pop();
if(c == ')' && topChar != '(')
return false;
if(c == ']' && topChar != '[')
return false;
if(c == '}' && topChar != '{')
return false;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println((new Solution()).isValid("()[]{}"));
System.out.println((new Solution()).isValid("([)]"));
}
}
队列
定义
队列是一种线性结构
只能从一端(队尾)添加元素,只能从另一端(队首)取出元素
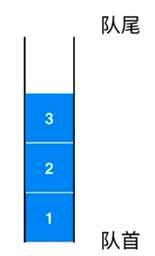
结论:队列是一种先进先出的数据结构(First in First out)

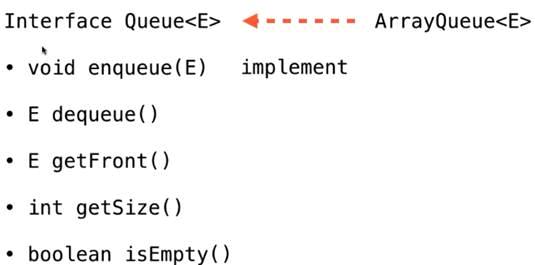
队列的实现
队列时间复杂度分析

Array
public class Array<E> {
private E[] data;
private int size;
// 构造函数,传入数组的容量capacity构造Array
public Array(int capacity){
data = (E[])new Object[capacity];
size = 0;
}
// 无参数的构造函数,默认数组的容量capacity=10
public Array(){
this(10);
}
// 获取数组的容量
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length;
}
// 获取数组中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 在index索引的位置插入一个新元素e
public void add(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
if(size == data.length)
resize(2 * data.length);
for(int i = size - 1; i >= index ; i --)
data[i + 1] = data[i];
data[index] = e;
size ++;
}
// 向所有元素后添加一个新元素
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
// 在所有元素前添加一个新元素
public void addFirst(E e){
add(0, e);
}
// 获取index索引位置的元素
public E get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Index is illegal.");
return data[index];
}
public E getLast(){
return get(size - 1);
}
public E getFirst(){
return get(0);
}
// 修改index索引位置的元素为e
public void set(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Index is illegal.");
data[index] = e;
}
// 查找数组中是否有元素e
public boolean contains(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 查找数组中元素e所在的索引,如果不存在元素e,则返回-1
public int find(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 从数组中删除index位置的元素, 返回删除的元素
public E remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
E ret = data[index];
for(int i = index + 1 ; i < size ; i ++)
data[i - 1] = data[i];
size --;
data[size] = null; // loitering objects != memory leak
if(size == data.length / 4 && data.length / 2 != 0)
resize(data.length / 2);
return ret;
}
// 从数组中删除第一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeFirst(){
return remove(0);
}
// 从数组中删除最后一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeLast(){
return remove(size - 1);
}
// 从数组中删除元素e
public void removeElement(E e){
int index = find(e);
if(index != -1)
remove(index);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Array: size = %d , capacity = %d\n", size, data.length));
res.append('[');
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
res.append(data[i]);
if(i != size - 1)
res.append(", ");
}
res.append(']');
return res.toString();
}
// 将数组空间的容量变成newCapacity大小
private void resize(int newCapacity){
E[] newData = (E[])new Object[newCapacity];
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++)
newData[i] = data[i];
data = newData;
}
}
ArrayQueue
public class ArrayQueue<E> implements Queue<E> {
private Array<E> array;
public ArrayQueue(int capacity){
array = new Array<>(capacity);
}
public ArrayQueue(){
array = new Array<>();
}
@Override
public int getSize(){
return array.getSize();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty(){
return array.isEmpty();
}
public int getCapacity(){
return array.getCapacity();
}
@Override
public void enqueue(E e){
array.addLast(e);
}
@Override
public E dequeue(){
return array.removeFirst();
}
@Override
public E getFront(){
return array.getFirst();
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append("Queue: ");
res.append("front [");
for(int i = 0 ; i < array.getSize() ; i ++){
res.append(array.get(i));
if(i != array.getSize() - 1)
res.append(", ");
}
res.append("] tail");
return res.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayQueue<Integer> queue = new ArrayQueue<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++){
queue.enqueue(i);
System.out.println(queue);
if(i % 3 == 2){
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println(queue);
}
}
}
}
Queue
public interface Queue<E> {
int getSize();
boolean isEmpty();
void enqueue(E e);
E dequeue();
E getFront();
}
引出一个问题
删除队首元素会引发O(n)的操作
因此提出指向一个队首和队尾的指针
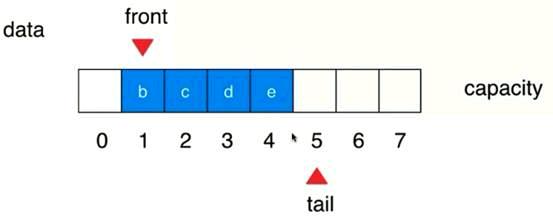
循环队列
Front和tail相等的时候队列为空
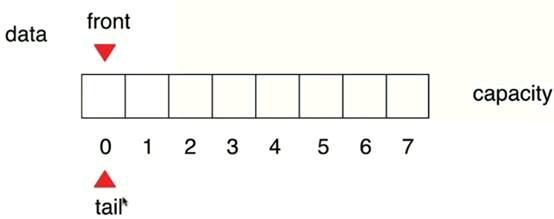
当往队首添加元素的时候
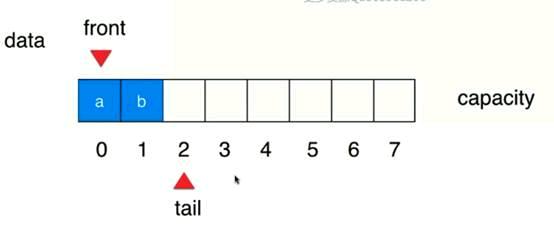
如果出现出队的同时又出现入队
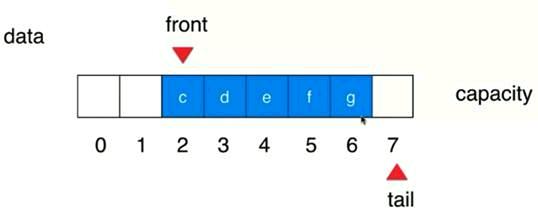
当队尾出入队到容量的极限的时候,会先去看一下front之前有没有位置,
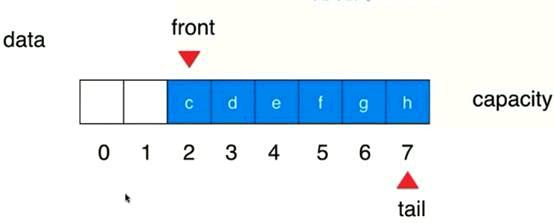
如果有空位
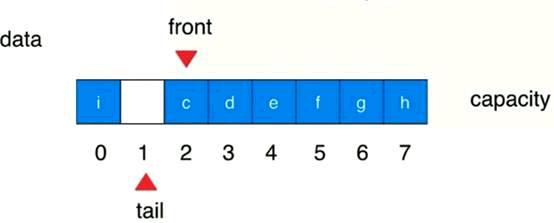
Tail会到回到容量的起始,再依次往后,(tail+1)%capacity(data.length)=front——》队列满,整个循环队列的结构是有意识地浪费了一个空间

解释一下循环队列的代码:
Newdata0-front
Newdata1-front+1
真正的队列偏移是front+i的,由于又是循环队列,因此防止数组越界,(front+i)%data.length
代码实现
public class LoopQueue<E> implements Queue<E> {
private E[] data;
private int front, tail;
private int size; // 有兴趣的同学,在完成这一章后,可以思考一下:
// LoopQueue中不声明size,如何完成所有的逻辑?
// 这个问题可能会比大家想象的要难一点点:)
public LoopQueue(int capacity){
data = (E[])new Object[capacity + 1];
front = 0;
tail = 0;
size = 0;
}
public LoopQueue(){
this(10);
}
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length - 1;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty(){
return front == tail;
}
@Override
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
@Override
public void enqueue(E e){
if((tail + 1) % data.length == front)
resize(getCapacity() * 2);
data[tail] = e;
tail = (tail + 1) % data.length;
size ++;
}
@Override
public E dequeue(){
if(isEmpty())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot dequeue from an empty queue.");
E ret = data[front];
data[front] = null;
front = (front + 1) % data.length;
size --;
if(size == getCapacity() / 4 && getCapacity() / 2 != 0)
resize(getCapacity() / 2);
return ret;
}
@Override
public E getFront(){
if(isEmpty())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Queue is empty.");
return data[front];
}
private void resize(int newCapacity){
E[] newData = (E[])new Object[newCapacity + 1];
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++)
newData[i] = data[(i + front) % data.length];
data = newData;
front = 0;
tail = size;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Queue: size = %d , capacity = %d\n", size, getCapacity()));
res.append("front [");
for(int i = front ; i != tail ; i = (i + 1) % data.length){
res.append(data[i]);
if((i + 1) % data.length != tail)
res.append(", ");
}
res.append("] tail");
return res.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
LoopQueue<Integer> queue = new LoopQueue<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++){
queue.enqueue(i);
System.out.println(queue);
if(i % 3 == 2){
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println(queue);
}
}
}
}
循环队列与数组队列的时间复杂度分析

import java.util.Random;
public class Main {
// 测试使用q运行opCount个enqueueu和dequeue操作所需要的时间,单位:秒
private static double testQueue(Queue<Integer> q, int opCount){
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
Random random = new Random();
for(int i = 0 ; i < opCount ; i ++)
q.enqueue(random.nextInt(Integer.MAX_VALUE));
for(int i = 0 ; i < opCount ; i ++)
q.dequeue();
long endTime = System.nanoTime();
return (endTime - startTime) / 1000000000.0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int opCount = 100000;
ArrayQueue<Integer> arrayQueue = new ArrayQueue<>();
double time1 = testQueue(arrayQueue, opCount);
System.out.println("ArrayQueue, time: " + time1 + " s");
LoopQueue<Integer> loopQueue = new LoopQueue<>();
double time2 = testQueue(loopQueue, opCount);
System.out.println("LoopQueue, time: " + time2 + " s");
}
}
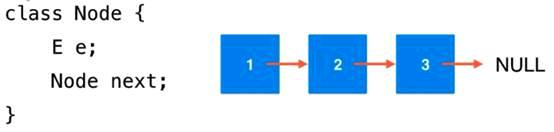
链表
前瞻课程:
内部类
链表是一种真正的动态数据结构

数据存储在“节点”(node)中
优点:真正的动态,不需要处理固定容量的问题,不需要跟动态数组一样,一下子new出来这么多的空间
缺点:丧失了随机访问的能力(无法如数组那样,根据索引查询元素,只能根据指向线索进行索引)
数组结构和链表结构的对比

动态链表基础结构
public class LinkedList<E> {
private class Node{
public E e;
public Node next;
public Node(E e, Node next){
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(E e){
this(e, null);
}
public Node(){
this(null, null);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return e.toString();
}
}
}
给链表中添加元素
在表头添加数据
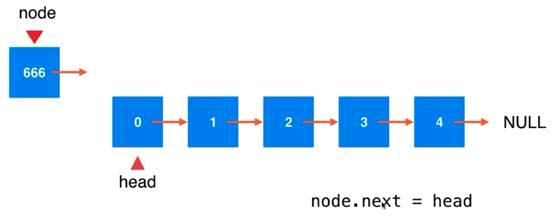
将head指向node
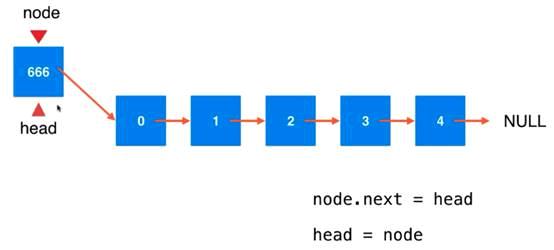
于是node就成为了该链表的head,进入链表中后,成为了链表的一部分
在链表指定索引处添加节点
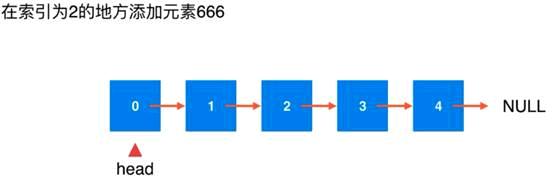
Head节点处有一个prev节点指标
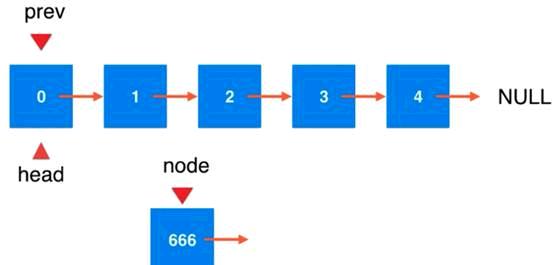
把这个prev插入的需要插入的节点:前一个节点
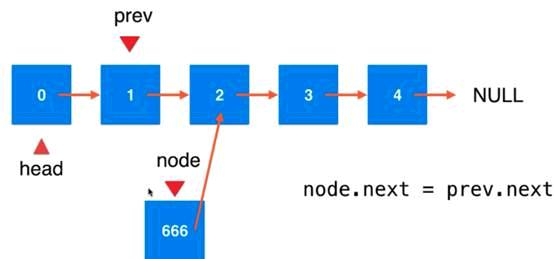
插入过程中关系的转换体现
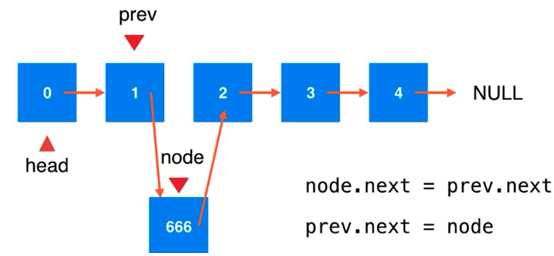
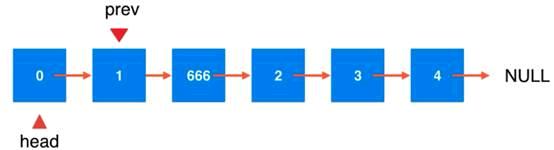
插入成功后的链表样式
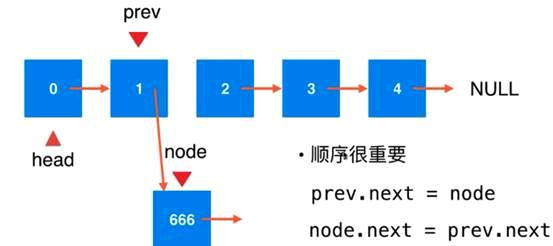
思考一下,执行插入的时候顺序能否发生变化
代码实现:
public class LinkedList<E> {
private class Node{
public E e;
public Node next;
public Node(E e, Node next){
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(E e){
this(e, null);
}
public Node(){
this(null, null);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return e.toString();
}
}
private Node head;
private int size;
public LinkedList(){
head = null;
size = 0;
}
// 获取链表中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 在链表头添加新的元素e
public void addFirst(E e){
// Node node = new Node(e);
// node.next = head;
// head = node;
head = new Node(e, head);
size ++;
}
// 在链表的index(0-based)位置添加新的元素e
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:)
public void add(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index.");
if(index == 0)
addFirst(e);
else{
Node prev = head;
for(int i = 0 ; i < index - 1 ; i ++)
prev = prev.next;
// Node node = new Node(e);
// node.next = prev.next;
// prev.next = node;
prev.next = new Node(e, prev.next);
size ++;
}
}
// 在链表末尾添加新的元素e
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
}
给链表使用虚拟头结点
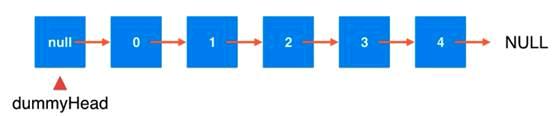
为链表添加一个虚拟的空的节点,注意,这个头结点是根本不存在的,是虚拟的,只是为了逻辑方便实现,添加的一个虚拟空的元素,否则就会对处理头结点有不同的逻辑,可以类别循环队列
public class LinkedList<E> {
private class Node{
public E e;
public Node next;
public Node(E e, Node next){
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(E e){
this(e, null);
}
public Node(){
this(null, null);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return e.toString();
}
}
private Node dummyHead;
private int size;
public LinkedList(){
dummyHead = new Node();
size = 0;
}
// 获取链表中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 在链表的index(0-based)位置添加新的元素e
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:)
public void add(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index > size){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index.");
}
Node prev = dummyHead;
for(int i = 0 ; i < index ; i ++){
prev = prev.next;
}
prev.next = new Node(e, prev.next);
size ++;
}
// 在链表头添加新的元素e
public void addFirst(E e){
add(0, e);
}
// 在链表末尾添加新的元素e
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
}
链表的遍历,查询和修改
对于链表来说,查询并非是一个常用操作,目前用于练习使用
Linkedlist
public class LinkedList<E> {
private class Node{
public E e;
public Node next;
public Node(E e, Node next){
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(E e){
this(e, null);
}
public Node(){
this(null, null);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return e.toString();
}
}
private Node dummyHead;
private int size;
public LinkedList(){
dummyHead = new Node();
size = 0;
}
// 获取链表中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 在链表的index(0-based)位置添加新的元素e
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:)
public void add(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index > size){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index.");
}
Node prev = dummyHead;
for(int i = 0 ; i < index ; i ++){
prev = prev.next;
}
prev.next = new Node(e, prev.next);
size ++;
}
// 在链表头添加新的元素e
public void addFirst(E e){
add(0, e);
}
// 在链表末尾添加新的元素e
public void addLast(E e){
add(size, e);
}
// 获得链表的第index(0-based)个位置的元素
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:)
public E get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size){
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Illegal index.");
}
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
for(int i = 0 ; i < index ; i ++)
cur = cur.next;
return cur.e;
}
// 获得链表的第一个元素
public E getFirst(){
return get(0);
}
// 获得链表的最后一个元素
public E getLast(){
return get(size - 1);
}
// 修改链表的第index(0-based)个位置的元素为e
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:)
public void set(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Illegal index.");
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
for(int i = 0 ; i < index ; i ++)
cur = cur.next;
cur.e = e;
}
// 查找链表中是否有元素e
public boolean contains(E e){
Node cur = dummyHead.next;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.e.equals(e))
return true;
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
// Node cur = dummyHead.next;
// while(cur != null){
// res.append(cur + "->");
// cur = cur.next;
// }
for(Node cur = dummyHead.next ; cur != null ; cur = cur.next)
res.append(cur + "->");
res.append("NULL");
return res.toString();
}
}
Main
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i ++){
linkedList.addFirst(i);
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
linkedList.add(2, 666);
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
}
从链表中删除元素
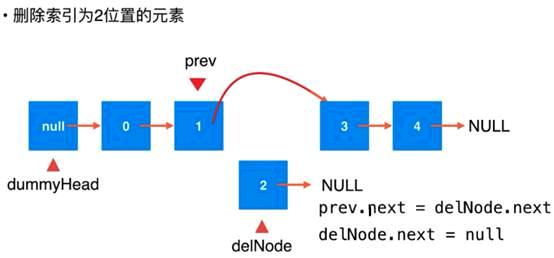
// 从链表中删除index(0-based)位置的元素, 返回删除的元素
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:)
public E remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
Node prev = dummyHead;
for(int i = 0 ; i < index ; i ++)
prev = prev.next;
Node retNode = prev.next;
prev.next = retNode.next;
retNode.next = null;
size --;
return retNode.e;
}
// 从链表中删除第一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeFirst(){
return remove(0);
}
// 从链表中删除最后一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeLast(){
return remove(size - 1);
}
// 从链表中删除元素e
public void removeElement(E e){
Node prev = dummyHead;
while(prev.next != null){
if(prev.next.e.equals(e))
break;
prev = prev.next;
}
if(prev.next != null){
Node delNode = prev.next;
prev.next = delNode.next;
delNode.next = null;
size --;
}
}
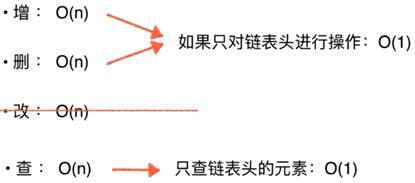
时间复杂度计算


 总结
总结
使用链表实现栈
Stack
Main
使用链表实现队列结构
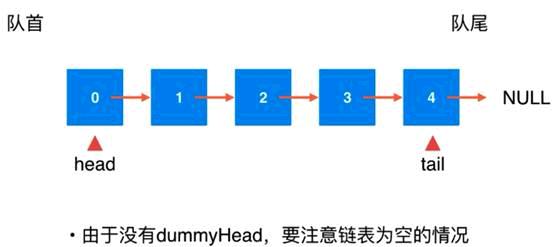
public class LinkedListQueue<E> implements Queue<E> {
private class Node{
public E e;
public Node next;
public Node(E e, Node next){
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(E e){
this(e, null);
}
public Node(){
this(null, null);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return e.toString();
}
}
private Node head, tail;
private int size;
public LinkedListQueue(){
head = null;
tail = null;
size = 0;
}
@Override
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
@Override
public void enqueue(E e){
if(tail == null){
tail = new Node(e);
head = tail;
}
else{
tail.next = new Node(e);
tail = tail.next;
}
size ++;
}
@Override
public E dequeue(){
if(isEmpty())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot dequeue from an empty queue.");
Node retNode = head;
head = head.next;
retNode.next = null;
//判断一下整个队列为空的情况
if(head == null)
tail = null;
size --;
return retNode.e;
}
@Override
public E getFront(){
if(isEmpty())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Queue is empty.");
return head.e;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append("Queue: front ");
Node cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
res.append(cur + "->");
cur = cur.next;
}
res.append("NULL tail");
return res.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args){
LinkedListQueue<Integer> queue = new LinkedListQueue<>();
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++){
queue.enqueue(i);
System.out.println(queue);
if(i % 3 == 2){
queue.dequeue();
System.out.println(queue);
}
}
}
}
package com.mylinkedlist;
public class LinkedList2<E> {
private class Node{
public E e;
public Node next;
public Node(E e, Node next){
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(E e){
this(e, null);
}
public Node(){
this(null, null);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
// return e.toString();
return "Node [e=" + e + ", next=" + next + "]";
}
}
private Node dummyHead;
private int size;
public LinkedList2(){
dummyHead = new Node();
size = 0;
}
// 获取链表中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 在链表的index(0-based)位置添加新的元素e
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用:)
public void insert(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index.");
}
Node prev = dummyHead;
for(int i = 0 ; i < index ; i ++) {
prev = prev.next;
}
prev.next = new Node(e, prev.next);
size ++;
}
// 在链表头添加新的元素e
public void addHead(E e){
insert(0, e);
}
// 在链表末尾添加新的元素e
public void addLast(E e){
insert(size, e);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "LinkedList2 [dummyHead=" + dummyHead + ", size=" + size + "]";
}
}